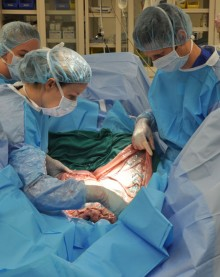
In an exciting advancement for eye treatment, CALEC surgery is revolutionizing the way we address severe corneal injuries. Developed at Mass Eye and Ear, this innovative procedure utilizes cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells to restore the corneal surface, offering new hope to patients suffering from previously untreatable conditions. The technique involves harvesting stem cells from a healthy eye and transplanting them into the damaged area, significantly improving both vision and comfort. As outlined in recent clinical trials, CALEC surgery has demonstrated a remarkable success rate, paving the way for a safer alternative to traditional corneal transplant methods. With its potential to transform corneal repair and enhance quality of life, CALEC surgery is undeniably a game-changer in ocular health.
Also known as cultivated limbal epithelial cell transfer, CALEC surgery presents a groundbreaking approach in the field of ocular regenerative medicine. This advanced technology leverages the body’s own stem cells to facilitate corneal regeneration, particularly beneficial for patients who have exhausted conventional eye treatment options. By focusing on the limbal region, where essential stem cells reside, this procedure aims to restore damaged corneal surfaces effectively. Whether referred to as stem cell-based techniques or innovative corneal restorative methods, this pioneering surgery not only has the potential to improve visual performance but also addresses chronic pain resulting from corneal disorders.
Introduction to CALEC Surgery: A Revolutionary Eye Treatment
The cultivation of autologous limbal epithelial cells, or CALEC surgery, represents a groundbreaking advancement in the field of ophthalmology, aiming to restore corneal surfaces affected by injuries that were previously deemed untreatable. Developed at Mass Eye and Ear, CALEC allows for the transplantation of stem cells from a healthy eye into the corneal surface of an injured eye, offering new hope to patients suffering from significant ocular damage. This innovative procedure highlights the important role that limbal epithelial cells play in maintaining a healthy cornea, as they are essential for its regeneration after sustaining trauma.
Ula Jurkunas and her team have pioneered this treatment, conducting a clinical trial that not only demonstrates the feasibility of CALEC surgery but also showcases its impressive success rates. With safety measures and meticulous protocols in place, the procedure has successfully restored the corneal surface in numerous patients, paving the way for future innovations in eye treatment options. As we delve deeper into the efficacy and methodology behind CALEC, it becomes evident that this surgery could redefine approaches to corneal repair in the coming years.
The Role of Stem Cell Therapy in Corneal Repair
Stem cell therapy stands at the forefront of modern medical advancements, especially in regenerative medicine for the eyes. In corneal repair specifically, the use of stem cells—particularly limbal epithelial cells harvested from a healthy eye—offers an innovative solution for patients suffering from limbal stem cell deficiency caused by traumatic injuries, chemical burns, or infections. These stem cells are crucial in restoring the corneal surface, as they have the unique ability to regenerate damaged tissues and restore visual clarity.
Through the lens of recent clinical trials, stem cell therapy’s potential is especially promising. Researchers have noted that CALEC achieves an effectiveness rate of over 90% in restoring the corneal surface, marking a significant milestone for patients with previously untreatable injuries. The implications of successfully integrating stem cell treatments into mainstream eye care are profound, as they can lead to a substantial decrease in the need for corneal transplants, which often involve lengthy waiting periods and potential complications.
Challenges and Limitations of CALEC Surgery
While the CALEC surgery presents a revolutionary step forward in eye treatments, it is not without its challenges and limitations. A key requirement for potential participants in the clinical trial is that they must possess only one affected eye from which stem cells can be harvested. This constraint limits the accessibility of the procedure for those suffering from bilateral corneal damage. Additionally, the need for further research and validation to broaden the applicability of CALEC is paramount, as scientists explore the possibility of utilizing stem cells from cadaveric donor eyes.
Jurkunas and her research team aim to overcome these obstacles by investigating allogeneic manufacturing processes that could enable the use of external donor cells for treatment. This evolution could significantly impact the number of patients eligible for CALEC treatment, addressing the pressing need for effective eye treatments for individuals facing severe corneal conditions.
Clinical Trials and Success Rates of CALEC
The recent clinical trials for CALEC surgery yield promising results, demonstrating impressive success rates in restoring corneal integrity among participants. Initial findings indicated that 50% of individuals experienced full corneal restoration within just three months, a figure that rose dramatically to 79% and 77% by the 12- and 18-month follow-ups, respectively. These statistics signal a bright future for CALEC surgery, suggesting that stem cell therapy can provide tangible improvements in vision for patients previously left with limited options.
Moreover, the safety profile of CALEC surgery has been closely monitored, revealing no serious adverse events, underscoring the treatment’s viability. While some minor complications were noted, they were easily managed and resolved quickly. The positive outcomes associated with the trial suggest that CALEC not only meets safety standards but also fulfills a significant need for innovative eye treatment solutions, further justifying the continuation of such research.
Broader Implications of Stem Cell Eye Treatments
The broader implications of therapies like CALEC extend beyond individual patient outcomes; they hold the potential to transform ophthalmic practices and standards of care globally. As researchers refine methodologies and expand trials to include larger patient populations, the insights gained could prompt a reevaluation of how we approach corneal repair and regeneration. This paradigm shift could lead to the establishment of new protocols that incorporate stem cell therapies into regular treatment practices.
Furthermore, the success of CALEC surgery may pave the way for similar approaches aimed at treating other forms of ocular damage and dysfunction. The pursuit of allogeneic options for stem cell harvesting could also improve accessibility, driving innovations in therapies for a wider range of eye conditions. Overall, the CALEC approach symbolizes a significant leap forward for regenerative medicine in ophthalmology, promising a brighter future for those affected by serious eye injuries.
Future Research Directions for CALEC Surgery
As CALEC surgery progresses, future research endeavors will be crucial in validating and expanding the efficacy of this treatment. Potential directions for subsequent studies may involve larger-scale clinical trials that encompass a diverse patient demographic, assessments of long-term outcomes, and multi-center studies designed to evaluate the consistency and reproducibility of results across different healthcare settings. Such thorough investigation could ultimately lead to widespread acceptance and application of this promising stem cell therapy.
Moreover, researchers are optimistic about exploring additional collaborations that can further enrich the clinical landscape surrounding CALEC surgery. By partnering with institutions focused on cellular therapy innovations, it may be possible to refine the graft manufacturing process, enhancing the overall quality and reliability of the stem cell treatments. This collaborative spirit could drive breakthroughs in overcoming current treatment limitations, ultimately expanding the horizon of what’s possible for patients with corneal injuries.
Understanding Limbal Epithelial Cells and Their Importance
Limbal epithelial cells are fundamental to the health and functionality of the cornea, serving as a critical resource for regeneration following injury. Located at the limbus, these cells act as a barrier and provide a smooth surface essential for vision quality. When these cells are depleted due to trauma or disease, patients may suffer from severe visual impairment and persistent discomfort, highlighting the importance of restoring this delicate balance through treatments like CALEC surgery.
Clinical advancements and research are increasingly focusing on the preservation and optimal utilization of limbal epithelial cells, reinforcing their role in contemporary eye treatment approaches. By understanding the mechanics of these cells and their regenerative capabilities, ophthalmologists can develop more refined surgical techniques and interventions aimed at restoring them, significantly enhancing rehabilitation outcomes for those with corneal damage.
Patient Experiences and Testimonials from CALEC Surgery
Patients who have undergone CALEC surgery often describe a transformative experience, not only in terms of restored vision but also in overall quality of life. Many report significant reductions in pain and an improved ability to engage in daily activities, which had previously been hindered by their corneal injuries. As word spreads about the successes of this procedure, more individuals are anticipated to seek out this innovative treatment as a viable option.
Additionally, testimonials highlight the emotional aspect of reclaiming one’s vision and the profound impact that CALEC has had on personal and professional lives. The compassion and dedication shown by the surgical teams at Mass Eye and Ear are frequently commended, showcasing the patient-centered approach that is becoming synonymous with this pioneering eye treatment.
Conclusion: The Future of Eye Treatments with CALEC Surgery
In conclusion, CALEC surgery represents not just a medical advancement but a beacon of hope for thousands of patients with debilitating corneal injuries. With over 90% success rates, this innovative form of stem cell therapy could truly redefine restoration practices in ophthalmology while setting new standards for patient care and outcome expectations. As research continues and the medical community draws valuable insights from ongoing trials, we can anticipate a future where corneal damage can be treated effectively and compassionately.
The path toward broader adoption of CALEC surgery is lined with exciting possibilities, emphasizing the importance of ongoing research, collaboration, and innovation in the field of eye treatment. As we refine our understanding and application of limbal epithelial cells, the horizon for advancements in ophthalmic care continues to expand, promising a brighter tomorrow for those facing challenges with their vision.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is CALEC surgery and how does it work for eye treatment?
CALEC surgery, or Cultivated Autologous Limbal Epithelial Cell surgery, is a revolutionary eye treatment that involves harvesting limbal epithelial cells from a healthy eye and using them to repair the corneal surface of a damaged eye. Developed at Mass Eye and Ear, this innovative procedure aims to restore vision and alleviate pain for patients suffering from corneal injuries that were once considered untreatable.
What are the benefits of CALEC surgery compared to traditional corneal transplants?
CALEC surgery offers distinct advantages over traditional corneal transplants by utilizing the patient’s own stem cells for repair, thus minimizing the risk of rejection. Clinical trials have shown that CALEC has a high success rate of over 90% in restoring the corneal surface, providing a safer and more effective alternative for patients with limbal stem cell deficiency.
Who can benefit from CALEC surgery?
Patients who have suffered from severe corneal injuries, such as those resulting from chemical burns or infections, may benefit from CALEC surgery. However, candidates must have only one affected eye to allow for the harvesting of healthy limbal epithelial cells from the other eye. This innovative procedure is particularly beneficial for individuals who have not responded well to other forms of eye treatment.
How long does it take to prepare for CALEC surgery?
The preparation for CALEC surgery includes a biopsy procedure to extract limbal epithelial cells, which are then cultured to create a graft. This manufacturing process typically takes about two to three weeks, during which the harvested cells are expanded into a suitable tissue graft before surgical transplantation into the damaged cornea.
Is CALEC surgery safe and what are the potential risks?
CALEC surgery has exhibited a high safety profile in clinical trials, with no serious adverse events reported. Minor complications, such as infections due to chronic conditions like contact lens use, have occurred but were resolved quickly. Ongoing studies aim to further evaluate the long-term safety and efficacy of this innovative eye treatment.
What are the results of the clinical trials for CALEC surgery?
Clinical trials for CALEC surgery have shown promising results, with over 90% of patients experiencing restoration of the corneal surface over an 18-month follow-up period. Success rates increased significantly at different intervals, highlighting the potential for CALEC to transform the treatment landscape for corneal injuries.
When will CALEC surgery be widely available for patients?
Currently, CALEC surgery is still in the experimental stage and is not widely available at Mass Eye and Ear or other U.S. hospitals. Further studies are needed before the treatment can be submitted for federal approval, but researchers are optimistic about future trials that may pave the way for broader access.
How does stem cell therapy play a role in CALEC surgery?
Stem cell therapy is integral to CALEC surgery, as it employs cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells to regenerate the damaged corneal surface. By leveraging the natural regenerative properties of these stem cells, CALEC offers a groundbreaking approach to treating patients with significant corneal damage.
What ongoing research is being conducted on CALEC surgery?
Ongoing research focuses on expanding the application of CALEC surgery by developing an allogeneic manufacturing process that could utilize limbal stem cells from cadaveric donor eyes. Future studies aim to explore larger patient populations and randomized-control designs to further validate the effectiveness and safety of this innovative eye treatment.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| What is CALEC Surgery? | Cultivated Autologous Limbal Epithelial Cells (CALEC) surgery is a stem cell therapy aimed at restoring corneal surfaces damaged by injury or disease. |
| Procedure Description | The process involves taking stem cells from a healthy eye, expanding them into tissue grafts, and then transplanting these grafts into the damaged eye. |
| Success Rates | The trial reported a success rate of 93% and 92% at 12 and 18 months, respectively, with 50% full restoration at three months. |
| Safety Profile | No serious adverse events reported; minor issues resolved quickly. One participant developed a bacterial infection unrelated to the transplant. |
| Next Steps | Future trials will involve larger populations and aim for FDA approval, expanding access to treatment. |
| Research Funding | The trial is funded by the National Eye Institute, indicating strong institutional support. |
Summary
CALEC surgery represents a groundbreaking advancement in the treatment of corneal injuries, previously deemed untreatable. This innovative stem cell therapy not only demonstrates remarkable effectiveness but also exhibits a strong safety profile, offering hope to patients suffering from severe corneal damage. With successful trials conducted at Mass Eye and Ear, CALEC surgery paves the way for further research aimed at securing FDA approval, potentially making this life-changing treatment accessible to a broader patient population.