Bile imbalance and liver cancer are emerging topics in the field of liver disease research, highlighting the intricate relationship between bile acid metabolism and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent form of liver cancer. Recent studies have uncovered a pivotal molecular switch that, when disrupted, can lead to the overproduction of bile acids, triggering inflammation and liver injuries that pave the way for cancer development. This breakthrough in understanding the mechanisms behind liver cancer treatment brings new hope for therapeutic interventions targeting bile acid regulation. Notably, the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway has been identified as a critical player, influencing how bile acids are metabolized and impacting liver health. By exploring these connections, researchers aim to create innovative solutions that could transform the future of liver disease treatment and prevention.
The correlation between bile secretion and malignancies of the liver, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma, sheds light on the nuances of liver function and pathological states. This imbalance in bile acids, coupled with the activation of specific cell signaling pathways such as YAP FXR, underscores the complexity of liver disease mechanisms. Understanding these relationships not only enhances the knowledge of bile acid dynamics but also opens avenues for developing novel strategies in liver cancer management. New research efforts are probing into the role of bile acids as signaling molecules, revealing their impact beyond digestion and into critical metabolic processes relevant to cancer progression. Thus, the exploration of bile metabolism and its cascading effects on liver health represents a vital frontier in cancer research.
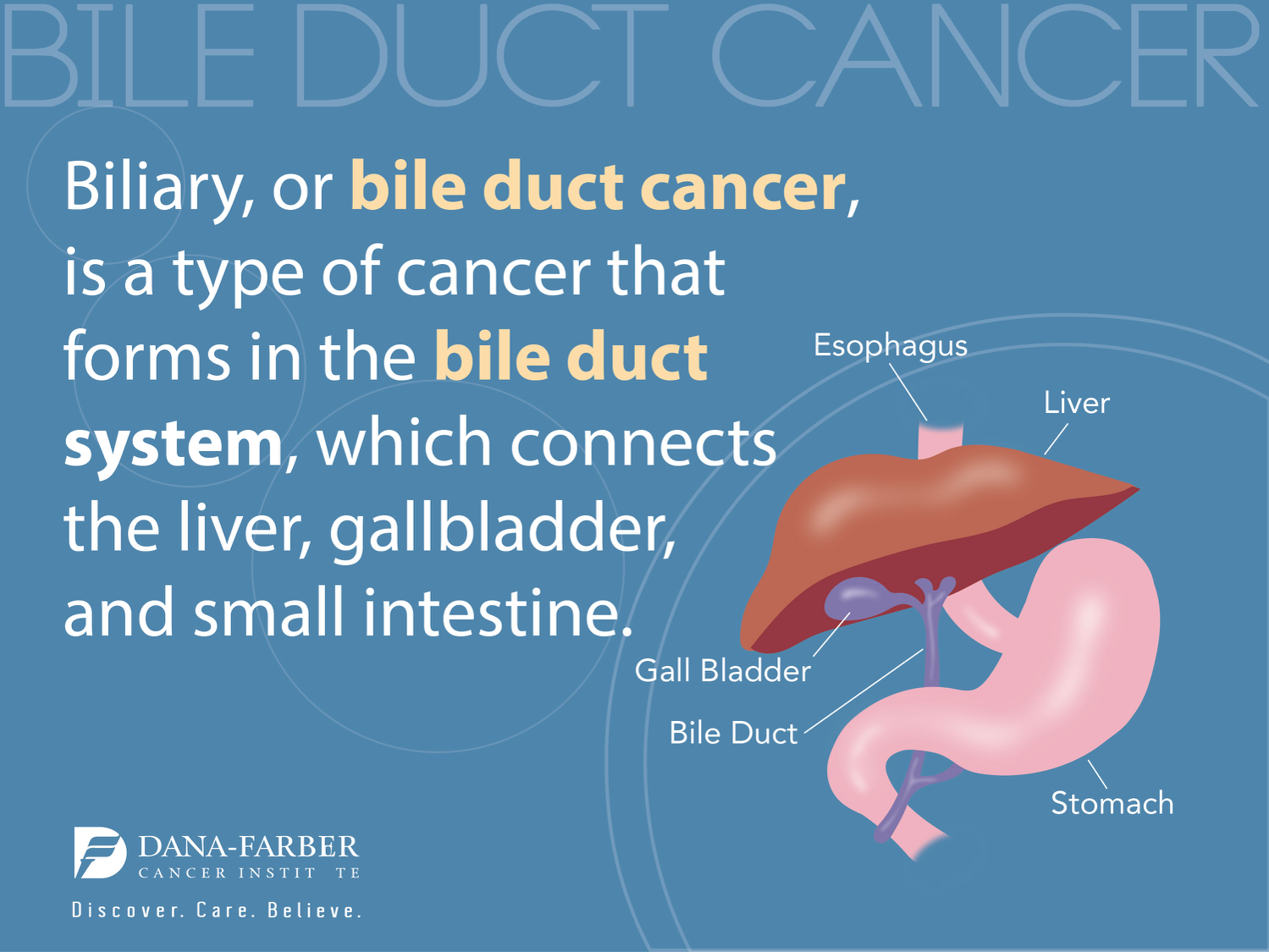
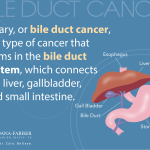
Understanding Bile Acid Metabolism and Its Role in Liver Health
Bile acid metabolism is vital for maintaining liver health and digestive efficiency. The liver produces bile acids that facilitate the digestion and absorption of fats in the small intestine. However, an imbalance in this metabolism can lead to various liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recent studies reveal that the regulation of bile acids is a tightly controlled process that, when disrupted, can result in liver inflammation and ultimately cancer. Researchers are focusing on understanding the functions of bile acids beyond their role in digestion, recognizing their importance in signaling pathways that regulate cellular metabolism and liver function.
The Hippo/YAP signaling pathway has emerged as a crucial player in bile acid metabolism and liver disease progression. When YAP is activated, it can disrupt the action of the Farnesoid X receptor (FXR), a critical regulator of bile acid homeostasis. This disruption leads to the overproduction of bile acids, resulting in liver injury and fibrosis. Understanding the molecular mechanisms behind this imbalance is essential for developing therapeutic interventions that could potentially reverse liver damage and mitigate the risks of liver cancer, strengthening the link between bile acid metabolism and liver health.
The Impact of YAP FXR Signaling on Hepatocellular Carcinoma
The YAP FXR signaling pathway is significant in the context of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Research indicates that YAP, typically associated with promoting cell growth, has a contrary role in the regulation of bile acid metabolism by acting as a repressor of FXR. When YAP inhibits FXR’s activity, it interferes with the body’s ability to manage bile acids effectively, leading to their accumulation in the liver, which can foster a pro-inflammatory environment conducive to cancer development. This surprising connection highlights the need for further investigation into how manipulating this pathway could provide new avenues for liver cancer treatment.
Therapeutic strategies that target the YAP FXR interaction could revolutionize liver cancer treatment. For instance, enhancing FXR function or stimulating bile acid excretion are potential approaches to mitigating liver damage and combating the progression of HCC. Promising results in experimental models demonstrate that these interventions can significantly reduce liver inflammation and cancer risk. As research continues to unravel the complexities of YAP and FXR in liver physiology, the hope is to translate these findings into effective treatments for patients suffering from liver diseases.
Innovative Treatment Approaches in Liver Disease Research
Ongoing liver disease research is unveiling innovative approaches for treating conditions such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). By investigating the molecular pathways involved in liver function and health, researchers are exploring new pharmacological agents that could target specific signaling cascades like the Hippo/YAP pathway. These agents aim to restore normal bile acid metabolism, potentially preventing inflammation and tumor formation within the liver. With advancements in molecular biology, there is a growing emphasis on developing precision medicine strategies that consider individual metabolic profiles and signaling patterns.
Furthermore, research teams are investigating how existing drugs can be repurposed to activate FXR or inhibit YAP to achieve favorable outcomes in liver disease treatment. The integration of genetic, cellular, and genomic approaches allows for a comprehensive understanding of how bile acids and their metabolic processes can be harnessed to prevent liver cancer. As more is understood about the underlying mechanisms of liver disease, the potential for innovative treatments that improve patient outcomes becomes increasingly promising, paving the way for a new era in liver disease management.
Exploring the Link Between Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer Therapy
The connection between bile imbalance and liver cancer therapy is becoming increasingly evident as researchers uncover the role bile acids play in liver pathophysiology. Current studies aim to establish how correcting bile acid dysregulation can not only prevent liver diseases but also serve as a therapeutic target for existing liver cancer treatments. By restoring balance in bile acid metabolism, it may be possible to alleviate inflammatory responses that contribute to tumor formation. This relationship emphasizes the need for ongoing research into the therapeutic potential of bile acid modifiers in liver cancer treatment.
One promising avenue in therapy involves the modulation of bile acids to influence tumor microenvironments positively. For patients diagnosed with HCC, ensuring optimal bile acid levels may enhance their response to conventional treatments, such as chemotherapy and targeted therapies. Additionally, the identification and development of drugs that can effectively stimulate FXR activity or inhibit harmful bile acid production could lead to significant advancements in ensuring better survival rates for patients with liver cancer. The integration of bile acid modulation into treatment protocols may represent a significant breakthrough in liver cancer therapy.
Key Molecular Findings Informing Liver Disease Treatment Strategies
Groundbreaking findings regarding key molecular mechanisms in liver disease have significant implications for treatment strategies, particularly concerning the role of bile acids. By understanding how molecules like YAP interact with FXR and disrupt bile acid metabolism, researchers can develop targeted therapies that address the root causes of liver dysfunction and hepatocellular carcinoma. These insights into the molecular switches that impact liver health pave the way for new pharmacological interventions aimed at restoring normal metabolic function and preventing cancer progression.
Additionally, the integration of molecular research with clinical observation can lead to more personalized treatment approaches in liver disease. By identifying biomarkers associated with bile acid imbalances, clinicians can tailor therapies to individual patients, ultimately improving efficacy. As the field advances, it is likely that the wealth of knowledge gained from studying the interplay of bile acids, YAP, and FXR will inform innovative and targeted interventions that enhance the prospects for patients battling liver diseases and cancer.
Future Prospects of Liver Cancer Treatment Research
The future of liver cancer treatment research looks promising, particularly with the identification of critical molecular pathways involved in bile acid metabolism. As the focus on the YAP FXR signaling pathway and its implications for hepatocellular carcinoma continues to grow, researchers are optimistic about discovering new pharmacological agents that could significantly improve treatment outcomes. The ability to modulate signaling pathways involved in bile acid regulation presents an exciting frontier in the fight against liver cancer, emphasizing the need for comprehensive research efforts.
Moreover, the collaboration between basic science and clinical research will be crucial in translating these molecular discoveries into effective therapeutic options for patients. As researchers work to better understand how to manipulate bile metabolism and its impact on liver cancer development, the potential for developing novel treatments that not only target existing cancer cells but also prevent new tumor formation becomes increasingly viable. This integration of knowledge across disciplines will be essential for developing effective strategies to combat liver cancer in the years to come.
Integrative Approaches in Liver Disease and Cancer Research
The rising complexity of liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma, necessitates integrative approaches that consider various factors influencing disease progression. By incorporating insights from cellular biology, metabolic science, and clinical practice, researchers are paving the way for comprehensive treatment strategies that address both the symptoms and the underlying causes of liver cancer. Understanding how various biological pathways are interconnected—particularly the role of bile acid metabolism in liver health—allows for more holistic treatment protocols that encompass lifestyle modifications, pharmacological interventions, and patient education.
This integrative strategy is fundamental in liver disease research, as it promotes collaboration among scientists, clinicians, and patients. By engaging diverse perspectives and expertise, the research community can devise innovative solutions to tackle the intricate challenges posed by liver diseases. Additionally, this collaborative environment fosters opportunities for clinical trials that explore the efficacy of new therapies targeting bile acid imbalances and their role in cancer prevention, thus enhancing the potential for breakthroughs in liver cancer treatments.
The Significance of Bile Acid Modulation in Liver Cancer Prevention
Bile acid modulation presents a significant opportunity for the prevention of liver cancer by targeting metabolic dysregulation within the liver. Recent findings indicate that maintaining balanced bile acid levels can mitigate risks associated with liver disease, including inflammation and fibrosis, which are precursors to hepatocellular carcinoma. Pharmacological agents that can effectively restore bile acid homeostasis may significantly lower the incidence of liver cancer, marking a new era in cancer prevention strategies.
Moreover, the research surrounding bile acids supports the concept that therapeutic interventions should aim to optimize bile acid signaling pathways. By enhancing the protective roles of bile acids and regulating their metabolism, scientists aim to not only prevent the onset of liver cancer but also improve overall liver function. Future therapies that harness the power of bile acids could serve as viable preventative measures against liver diseases, reinforcing their importance in both research and clinical applications.
Advancements in Understanding Cell Signaling Related to Liver Cancer
Advancements in our understanding of cell signaling pathways, particularly in relation to liver cancer, have been pivotal in reshaping therapeutic strategies. Researchers are increasingly focusing on the interplay between various signaling molecules, such as YAP and FXR, and their roles in regulating liver function and cancer progression. This deepened knowledge provides insights that can be translated into targeted therapies aimed at specific molecular mechanisms involved in liver cancer.
By examining how disruptions in cell signaling can contribute to bile imbalance and liver disease, scientists can identify potential therapeutic targets that could lead to more effective interventions for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. The ongoing research into these signaling pathways emphasizes the importance of developing an integrated understanding of how various molecular factors cooperate in the development of liver cancer, paving the way for innovative treatment approaches that can improve patient outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does bile imbalance relate to liver cancer?
Bile imbalance disrupts bile acid metabolism, which can lead to liver injury, inflammation, and ultimately hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common type of liver cancer. The regulation of bile acids is crucial for liver health, and any disruption can initiate cancerous changes.
What role does YAP FXR signaling play in liver cancer treatment?
YAP FXR signaling is essential in regulating bile acid metabolism and promoting liver cancer progression. Inhibiting the repressive function of YAP or enhancing FXR function may yield new treatments for liver cancer by restoring bile acid homeostasis.
Can bile acid metabolism influence hepatocellular carcinoma outcomes?
Yes, disrupted bile acid metabolism can lead to increased bile acid accumulation in the liver, resulting in fibrosis and inflammation, which are critical steps in the progression to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Therefore, managing bile acidosis is vital for liver cancer prevention.
What are the implications of bile imbalance in liver disease research?
Bile imbalance highlights crucial pathways and mechanisms that contribute to liver diseases, including the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Research focusing on bile acid signaling may uncover novel therapeutic targets for interventions in liver disease.
What advancements are being made in liver cancer treatment related to bile acids?
Recent studies are exploring pharmacological methods to enhance FXR function and promote bile acid excretion. These advancements may offer new treatment avenues for liver cancer by correcting metabolic imbalances associated with bile acids.
How might enhancing FXR function help with liver cancer?
Enhancing FXR function may restore proper bile acid metabolism and prevent the damaging cycle of bile accumulation in the liver, which can lead to cancerous changes and fibrosis. This presents a promising approach for liver cancer treatment.
What is the significance of hepatocellular carcinoma in bile disorder research?
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most prevalent form of liver cancer and serves as a critical focus in bile disorder research, particularly in understanding how bile acid imbalances contribute to tumor formation and liver disease progression.
What does the disruption of bile acid homeostasis mean for liver health?
Disruption of bile acid homeostasis can result in increased bile acid levels in the liver, leading to chronic inflammation, fibrosis, and an elevated risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), indicating the importance of maintaining bile balance for liver health.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance | Imbalances in bile acids can trigger liver diseases, including liver cancer. |
| Key Molecular Switch | A critical regulatory switch affecting bile acid metabolism was identified. |
| YAP and FXR | YAP can repress FXR, leading to bile acid overproduction and liver cancer. |
| Potential Treatments | Blocking YAP’s repressive effects could lead to new liver cancer treatments. |
| Research Support | Study supported by NIH and the National Cancer Institute, led by researchers at Harvard. |
Summary
Bile imbalance and liver cancer have been definitively linked through recent research, showing how disruptions in bile acid levels can lead to serious liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma. The identification of a key molecular switch, YAP, which represses the essential bile acid sensor FXR, highlights the complexity of liver metabolism and its implications for cancer treatment. This finding opens avenues for pharmaceutical interventions aimed at restoring bile acid balance, crucial for preventing liver diseases. Consequently, this study fosters hope for effective liver cancer therapies in the future.