TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s is emerging as a revolutionary approach to combat Alzheimer’s disease treatment, leveraging the power of the immune system to restore cognitive function. Recent studies have indicated that inhibiting TIM-3, a checkpoint molecule, can free microglia—brain immune cells—to actively clear amyloid plaques associated with neurodegeneration. This innovative therapy draws parallels from successful cancer immunotherapy, which also manipulates checkpoint molecules for enhanced immune response. Specifically, by reducing TIM-3 expression, researchers observed significant improvements in memory and cognitive performance in mouse models of Alzheimer’s, highlighting its potential as a viable option for combating neuroinflammation. As research advances, the intersection of immune function and Alzheimer’s presents exciting possibilities for future treatments, paving the way for a new era in neuroinflammation therapy.
The TIM-3 pathway presents a promising frontier in addressing the challenges posed by neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease. This cutting-edge approach not only focuses on the inhibitory actions of TIM-3 but also explores how altering these immune responses can mitigate the damage caused by amyloid plaques in the brain. By looking at the genetic influences of TIM-3, researchers are uncovering new avenues for therapy that may translate into effective solutions for cognitive decline. The findings suggest a significant link between immune system dynamics and Alzheimer’s disease, reinforcing the need for integrated strategies that enhance microglial activity and reduce neuroinflammation. As this research unfolds, alternatives to traditional methods are becoming increasingly vital in the quest for effective Alzheimer’s treatments.
Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease: The Role of the Immune System
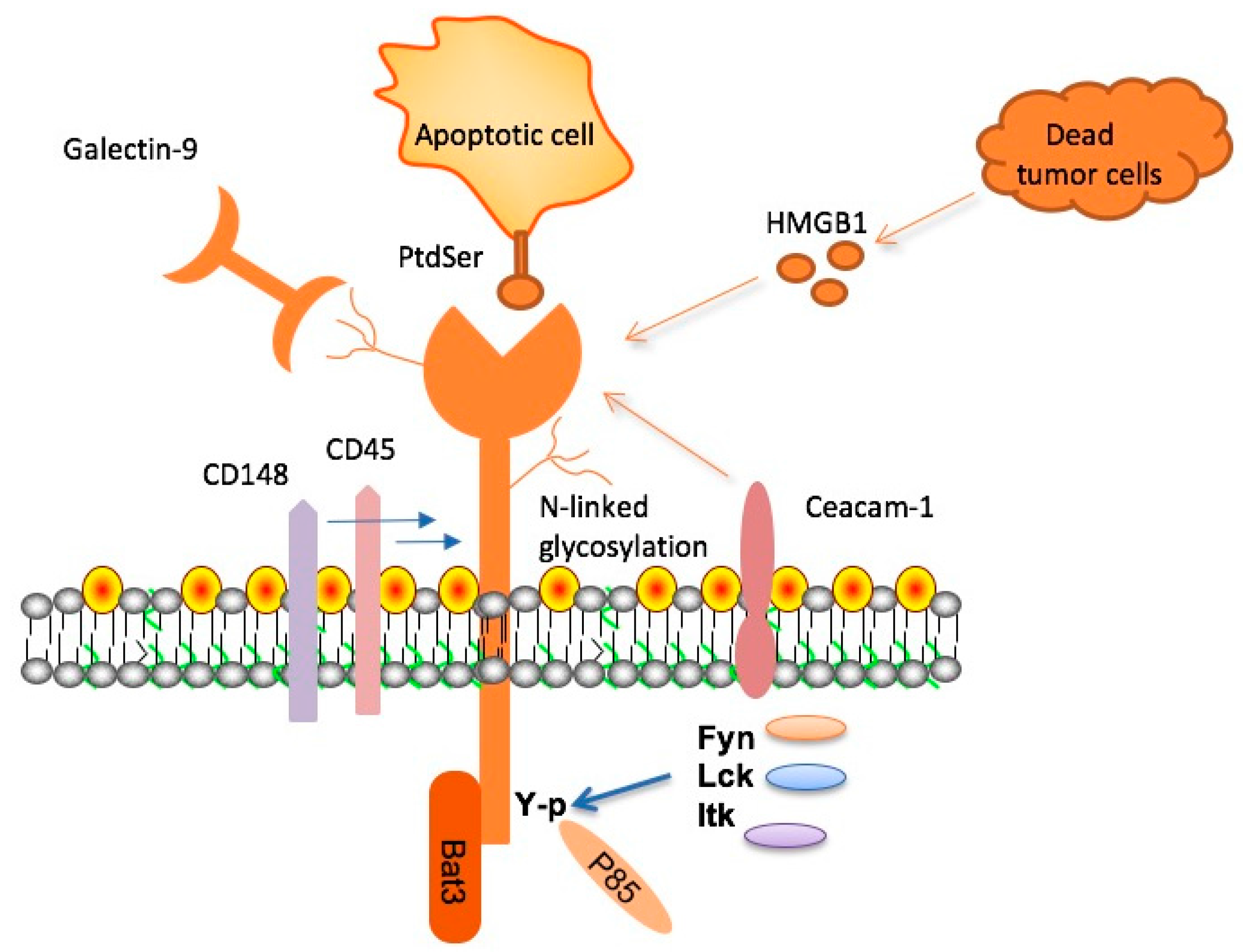
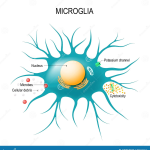
Alzheimer’s disease is a complex neurodegenerative condition characterized by the accumulation of amyloid plaques in the brain, leading to progressive cognitive decline. Central to our understanding of Alzheimer’s is the role of the immune system, particularly the brain’s resident immune cells known as microglia. These cells are tasked with clearing debris and maintaining neuronal health, but in the context of Alzheimer’s, they become dysfunctional. The presence of amyloid plaques triggers microglial activation, yet paradoxically, these cells often fail to clear the very plaques they are supposed to eliminate. This dysfunction is partly due to the increased expression of inhibitory checkpoint molecules like TIM-3, which restrain microglial activity and worsen cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s patients.
Recent research highlights how TIM-3 obstructs the ability of microglia to effectively respond to amyloid deposits, resulting in ongoing neuroinflammation. This process not only contributes to the buildup of plaques but also exacerbates memory loss and other cognitive issues associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Perturbing the regulation of the immune response in the brain highlights a possible therapeutic avenue that could modify the course of Alzheimer’s treatment, representing a significant shift from conventional strategies that mainly focus on amyloid plaque reduction.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s disease and how does it work?
TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s disease focuses on inhibiting the TIM-3 checkpoint molecule. TIM-3, which is overexpressed in microglia, inhibits their ability to clear amyloid plaques in the brain, which are characteristic of Alzheimer’s. By blocking TIM-3, microglia can better attack these plaques, potentially improving memory function in patients.
What role does TIM-3 play in Alzheimer’s disease treatment strategies?
In Alzheimer’s disease treatment strategies, TIM-3 is significant as it is linked to the immune response. It acts as an inhibitory molecule that prevents microglia from effectively removing plaques. Thus, targeting TIM-3 with therapy may enhance the immune system’s ability to combat Alzheimer’s associated neuroinflammation and improve cognitive functions.
How does TIM-3 therapy differ from traditional Alzheimer’s disease treatments?
TIM-3 therapy differs from traditional Alzheimer’s disease treatments by targeting immune system mechanisms instead of just addressing symptoms or amyloid beta levels. While many conventional treatments focus on reducing amyloid plaque accumulation, TIM-3 therapy aims to reactivate microglia, enabling them to clear existing plaques and restore cognitive functions.
What are the implications of TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s patients?
The implications of TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s patients are promising, as preliminary studies indicate that blocking TIM-3 may lead to improved plaque clearance by microglia and enhanced memory functions. This therapy could serve as a novel approach to reduce neuroinflammation and address the root causes of cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s patients.
What evidence supports the use of TIM-3 therapy in Alzheimer’s disease research?
Evidence supporting TIM-3 therapy in Alzheimer’s disease research includes studies where genetically modifying mice to lack the TIM-3 gene resulted in improved plaque clearance and cognitive function. These findings suggest that inhibiting TIM-3 allows microglia to engage more actively in combatting Alzheimer’s related neurodegeneration.
Are there any clinical trials for TIM-3 therapy in treating Alzheimer’s disease?
Yes, researchers are exploring the potential of TIM-3 therapies through various preclinical and clinical trials. The next steps involve testing human anti-TIM-3 antibodies in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models to assess their effectiveness in halting plaque development and improving cognitive performance.
How can TIM-3 therapy impact the role of microglia in Alzheimer’s?
TIM-3 therapy can significantly impact microglial function in Alzheimer’s disease by reducing inhibitory signals that prevent these immune cells from clearing amyloid plaques. By enhancing microglial activity through TIM-3 blockade, this therapy has the potential to alleviate neuroinflammation and support better cognitive health.
What is the genetic connection of TIM-3 with Alzheimer’s disease?
The genetic connection of TIM-3 with Alzheimer’s disease lies in the polymorphisms found in the HAVCR2 gene, which encodes TIM-3. Studies have shown that individuals with these genetic variations exhibit higher TIM-3 expression on microglia and an increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease, linking the immune response directly to disease progression.
What types of molecules are being researched for TIM-3 therapy in Alzheimer’s?
Research on TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s is focusing on anti-TIM-3 antibodies and small molecules that can inhibit TIM-3’s function. These agents aim to enhance the immune response against amyloid plaques in the brain, which could potentially lead to novel and more effective treatments for Alzheimer’s disease.
What challenges does TIM-3 therapy face in Alzheimer’s disease treatment?
TIM-3 therapy in Alzheimer’s disease faces challenges such as ensuring that therapies effectively target brain areas without adverse effects, as well as overcoming the complexities of neuroinflammation. Additionally, translating findings from animal studies to humans requires careful study design and monitoring in clinical trials.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Introduction of TIM-3 Therapy | Offers hope for Alzheimer’s treatment, linked to immune checkpoint molecules. |
| Mechanism of Action | Blocking TIM-3 allows microglia to clear amyloid plaques, improving memory and cognition in mice. |
| Prevalence of Late-Onset Alzheimer’s | 90%-95% of Alzheimer’s cases are late-onset, TIM-3 is a genetic risk factor. |
| Microglia Function | Microglia are brain immune cells that prune synapses but become dysfunctional due to TIM-3. |
| Potential Therapy | Use of anti-TIM-3 antibodies or small molecules to inhibit TIM-3’s function. |
| Current Research Developments | Testing anti-TIM-3 effects in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. |
Summary
TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s represents a promising new approach in tackling this neurodegenerative disease. By inhibiting the TIM-3 checkpoint molecule, researchers have demonstrated the potential to enhance the immune response against amyloid plaques in the brain, leading to improvements in cognitive function in preclinical models. This could pave the way for groundbreaking treatments that address the root causes of Alzheimer’s rather than just alleviating symptoms.