Bile imbalance liver cancer emerges as a significant health concern due to its alarming connection with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the predominant type of liver cancer. Recent research has highlighted how disruptions in bile acid metabolism can trigger severe liver diseases, making the understanding of this condition crucial for effective intervention and liver cancer treatment. By investigating the YAP FXR pathway, scientists have begun to unravel how bile acid imbalances can foster an environment conducive to liver injury and cancer progression. The insights from these studies pave the way for innovative treatments aimed at restoring bile homeostasis and mitigating the risks associated with liver disease. As liver disease research continues to evolve, the pivotal role of bile in maintaining liver health becomes increasingly clear.
The relationship between disrupted bile production and liver malignancies has opened new avenues for medical research, particularly in regards to hepatocellular carcinoma and other liver-related conditions. When bile acids, which are essential for fat digestion, are improperly regulated, they can lead to serious health issues including inflammation and fibrosis of the liver. Recent investigations into the molecular mechanisms at play, notably the integration of the YAP pathway and bile acid regulation, shed light on potential therapies for treating liver cancer. Additionally, understanding the complex functions of bile acids as both digestive aids and metabolic regulators can inform future liver disease research and treatment innovations. The ongoing quest to stabilize bile acid levels offers hope for enhanced patient outcomes in the realm of liver cancer.
Understanding Bile Imbalance and Its Relation to Liver Cancer
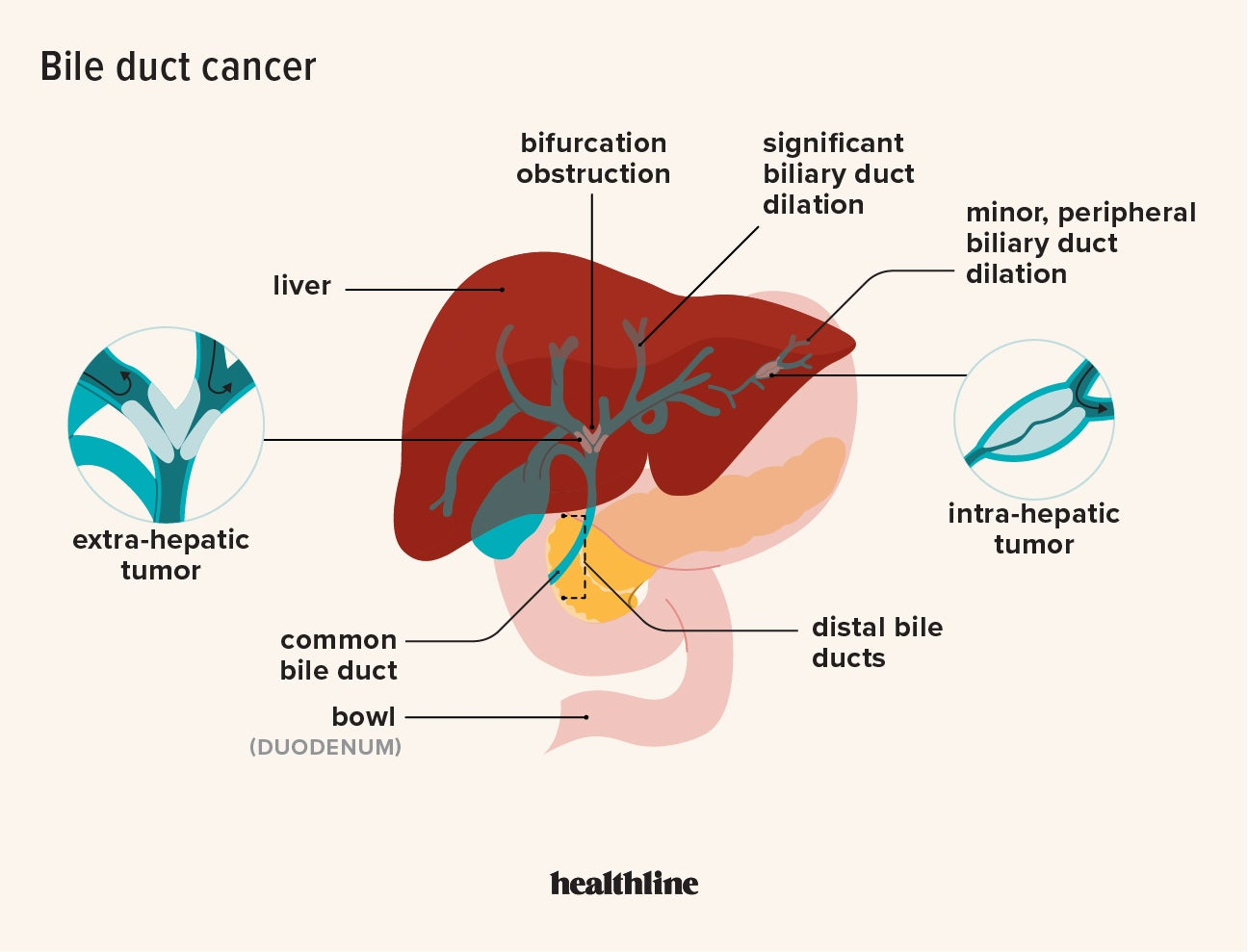
Bile imbalance is a crucial factor that contributes to various liver diseases, notably hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The liver’s unique responsibility in bile production is not just limited to aiding fat digestion; it also plays a significant role in regulating metabolic processes through bile acids. When these bile acids are not produced or regulated correctly, it can lead to dire health consequences, including liver inflammation and cancer. The research conducted by Yingzi Yang and her team highlights the critical nature of this bile acid regulation, shedding light on how imbalances can pave the way for tumor formation.
The implications of these findings underscore the importance of maintaining bile acid homeostasis. Disruptions often stem from molecular switch variances, particularly in the YAP FXR pathway. Uncontrolled YAP activity is shown to paralyze the FXR receptor, leading to an accumulation of bile acids in the liver. This accumulation not only instigates inflammation but also sets a pathway toward the development of liver cancer. Understanding this balance opens doors for new treatment avenues targeting bile acid metabolism, potentially inhibiting tumor development in patients predisposed to liver diseases.
The Role of the YAP FXR Pathway in Liver Cancer Treatment
The YAP FXR pathway stands out as a significant molecular mechanism in the context of bile imbalance and liver cancer. Research indicates that YAP can act counter-intuitively as a repressor rather than an enhancer in liver tumor biology. By inhibiting the crucial FXR receptor, involved in maintaining bile acid levels, YAP activation leads to increased bile acid production, promoting liver damage and subsequently HCC. Targeting this pathway offers an exciting frontier for liver cancer treatment, as easing the repression caused by YAP could restore FXR function and prevent the cascade of liver inflammation and fibrosis.
In therapeutic terms, the opportunity to manipulate this pathway for liver cancer prevention is immensely valuable. Experimental models have shown promising results when FXR is activated or HDAC1’s repression of YAP is inhibited. These interventions not only reduce liver damage but also slow cancer progression effectively. Thus, researchers are now focusing on pharmacological methods to stimulate FXR, positioning this research as a potential game-changer in liver cancer treatment approaches.
Bile Acid Metabolism: A Pathway to Innovative Liver Disease Therapeutics
Bile acid metabolism is emerging as a vital area of focus in liver disease research due to its profound effects on liver function and health. The dynamic between bile acids and liver health is complex, wherein disturbances in bile acid levels can trigger a multitude of liver diseases including HCC. Understanding these metabolic pathways is essential, as they may hold the key to uncovering efficacious liver disease therapeutics. The studies led by the Yang Laboratory serve as a reminder of the intricate biological processes involved in liver metabolism and their implications for disease emergence.
Researchers are now exploring novel drugs that can effectively target bile acid pathways, offering a new lens through which liver disease management can be approached. By enhancing the export of bile acids or boosting FXR activity, potential therapies could not only prevent liver cancer but also promote overall liver health. This warrants comprehensive investigation, as addressing bile acid metabolism may provide a robust strategy to counteract the growing incidences of liver disease globally.
Implications of Yang’s Research on Liver Disease Treatment
The innovative research by Yingzi Yang highlights significant implications for future liver disease treatments, particularly concerning the intricate relationship between bile imbalance and liver cancer. As understanding deepens around how YAP regulates bile acid metabolism and liver health, new therapeutic approaches can emerge. For instance, pharmacological agents that enhance FXR function may redefine treatment pathways for affected individuals, giving hope to those facing the dire consequences of liver cancer.
Furthermore, as this research expands our knowledge base, it could lead to patient-specific treatment plans aimed at correcting bile acid imbalances. Such advancements would not only be revolutionary for hepatology but also set a precedent for personalized medicine in treating liver conditions. By focusing on tailored treatments that consider an individual’s bile metabolism profile, healthcare providers can improve outcomes and enhance the quality of life for patients battling liver diseases.
The Connection Between Liver Health and Hormonal Regulation
Bile acids serve more than just a digestive purpose; they perform complex roles in hormonal regulation and metabolic control. The link between liver health and hormonal balance signifies the importance of addressing bile acid metabolism in liver disease treatments. Disruptions to this system can not only lead to liver inflammation but also signal broader metabolic dysfunctions, potentially resulting in severe health conditions like HCC. Thus, understanding this connection is vital for developing holistic liver disease therapies centered around metabolic pathways.
Research into bile acid’s hormonal functions reveals new aspects of liver disease that can be targeted therapeutically. For example, if therapies can correct the overproduction or improper signaling of bile acids, it could mitigate the risks associated with liver cancer. As ongoing studies delve deeper into the hormonal roles of bile acids, insights will continue to emerge, guiding the creation of multifaceted treatment strategies for liver diseases influenced by metabolic dysfunction.
Exploring Novel Pharmacological Approaches to Liver Cancer
The quest for novel pharmacological intervention targeting liver cancer has gained momentum with discoveries relating to bile acid metabolism. By targeting the YAP FXR pathway, researchers are identifying multiple untapped avenues for liver cancer therapy. Enhancing FXR function or understanding the complex interplay of bile acids offers potential for pharmacological solutions that may considerably diminish the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma. These innovative approaches reveal a promising shift toward more effective and tailored treatments for liver diseases.
Moreover, the research indicates that pharmacological modulation of bile acid pathways can lead to profound impacts on liver pathology. Approaches that block YAP’s repressive actions or enhance bile acid secretion through the FXR receptor demonstrate potential in reducing liver damage. Thus, the future of liver cancer treatment may not only involve conventional methods such as surgery or chemotherapy, but also a detailed pharmacological understanding of bile acid metabolism, ensuring a comprehensive fight against liver disease.
The Importance of Liver Disease Research in Advancing Healthcare
The growing body of research surrounding liver diseases highlights the critical need for innovative healthcare solutions. Studies unveiling the links between bile imbalance and hepatocellular carcinoma illustrate the broader implications of liver disease on public health. Comprehensive research is fundamental in identifying causal mechanisms behind liver disease, guiding the development of new therapies and screening protocols. As healthcare systems evolve, investing in liver disease research becomes vital for early diagnosis and intervention, ultimately saving lives.
Moreover, continuous research fosters a better understanding of the socio-economic impacts of liver diseases, such as those stemming from bile acid imbalance. As insights into liver health deepen, healthcare policies can evolve to prioritize funding for liver research initiatives. A committed focus on liver disease not only enriches clinical knowledge but also ensures patients receive cutting-edge treatments that incorporate recent scientific advancements, shaping a healthier future.
Integrating Multidisciplinary Approaches to Liver Cancer Research
Integrating multidisciplinary strategies in liver cancer research paves the way for comprehensive understanding and treatment of liver diseases. The collaboration of molecular biologists, pharmacologists, and clinical researchers creates a rich platform for exploring the mechanisms underpinning bile acid metabolism and its connection to liver cancer. Such an integrative approach enables a fuller perspective regarding the cellular and systemic responses to liver dysfunction, leading to more effective treatment methodologies.
By pooling diverse expertise, this holistic approach fosters innovative therapeutic solutions targeting liver cancer and related metabolic disorders. Research initiatives like those by the Yang Laboratory emphasize the need for collaboration across various scientific disciplines. In doing so, advancements in liver cancer therapies become not only aspirational goals but achievable realities fueled by collective intellectual engagement and integrated health solutions.
Future Perspectives in Liver Cancer Prevention and Management
The future of liver cancer prevention and management is bright, especially with groundbreaking research focusing on bile acid metabolism and its implications. As scientists pave the way toward novel intervention strategies, the understanding of how to balance bile acid levels and mitigate their harmful effects in liver disorders becomes paramount. Wider adoption of these discoveries into clinical practice will enhance current treatment paradigms, ultimately improving patient outcomes in liver disease.
Moreover, continued advancements in research methodologies will likely yield even better insights into liver health. Emphasis on personalized medicine approaches—tailoring treatment based on individual metabolic profiles—will ensure that therapies are not just effective, but are also holistic and aligned with an individual’s unique health needs. The collective focus on improving liver health through understanding bile metabolism marks a pivotal moment in medical research, setting the stage for pioneering prevention strategies and enhanced therapeutic options.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between bile imbalance and liver cancer?
Bile imbalance, characterized by abnormal bile acid levels, has been linked to liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Disruptions in bile acid metabolism can lead to liver injury and inflammation, ultimately increasing the risk of developing liver cancer.
How do bile acids influence liver cancer treatment options?
Bile acids play a crucial role in liver metabolism, and their imbalance can trigger liver diseases like HCC. Understanding bile acid metabolism and the YAP FXR pathway may lead to new liver cancer treatment options by targeting bile acid homeostasis and reducing cancer progression.
What role does the YAP FXR pathway play in bile acid metabolism and liver cancer?
The YAP FXR pathway is significant in regulating bile acid metabolism. Research shows that YAP can repress FXR, leading to an excess of bile acids that contribute to liver inflammation and fibrosis, paving the way for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Modulating this pathway could open new avenues for liver cancer therapies.
How can enhancing FXR function help prevent bile imbalance related to liver cancer?
Enhancing FXR function can help restore bile acid homeostasis, thus preventing the bile imbalance associated with liver cancer. By activating FXR, it is possible to reduce bile acid accumulation in the liver, thereby decreasing the risk of liver injury and subsequent hepatocellular carcinoma.
What research is being done on bile acid metabolism in relation to liver disease?
Current liver disease research focuses on the intricate regulation of bile acid metabolism and its connection to liver cancer. Studies, like those led by Yingzi Yang, investigate how disruptions in bile acid homeostasis, particularly through pathways like YAP and FXR, contribute to diseases including hepatocellular carcinoma.
Are there pharmacological approaches being explored to address bile imbalance in liver cancer patients?
Yes, researchers are exploring pharmacological approaches that stimulate FXR to address bile imbalance and its consequences in liver cancer patients. By focusing on enhancing bile acid excretion and restoring homeostasis, these treatments aim to mitigate liver damage and reduce the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer | A critical imbalance in bile acids can lead to liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This condition occurs when the liver does not maintain proper bile acid levels. |
| Key Molecular Switch | A study identified a key molecular switch that regulates bile acid metabolism and may lead to new treatment interventions for liver cancer. |
| Role of YAP | YAP (Yes-associated protein) promotes tumor formation and regulates bile acid metabolism, acting as a repressor that interferes with FXR (Farnesoid X receptor) function. |
| FXR Dysfunction | Dysfunction in FXR due to YAP activation leads to bile acid overproduction, liver inflammation, and fibrosis, ultimately resulting in liver cancer. |
| Potential Treatments | Enhancing FXR function or promoting bile acid excretion may halt the damaging cycle caused by YAP and offer pharmacological solutions for liver cancer treatment. |
Summary
Bile imbalance linked to liver cancer is a critical concern in hepatology, as disruptions in bile acid metabolism have significant implications for liver health. Recent studies reveal that this imbalance can trigger liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma, emphasizing the need for further research into regulatory mechanisms and potential therapeutic interventions.