Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked significant debate among nutritionists and health experts, leading many to explore the true nature of sugar’s effects on our bodies and minds. While it is classified as a non-addictive substance according to strict clinical definitions, many people experience intense sugar cravings, particularly when consuming processed foods laden with added sugars. The health effects of sugar can mimic those of addictive substances, with individuals reporting withdrawal-like symptoms when they cut back on their sugar intake, such as headaches and anxiety. Understanding the complexities of sugar’s role in our diets can help us navigate our eating habits and take control of our cravings.
Is sugar a substance we can become hooked on? Exploring the nuances surrounding sugar reveals how it can elicit strong cravings and compulsive behaviors similar to those induced by more commonly accepted addictive substances. Often found in ultra-processed foods, sugar not only plays a role in the pleasure response of our brains but can also lead to complications like sugar withdrawal symptoms when we attempt to reduce its consumption. As society grapples with the health implications of sugary diets, it becomes imperative to unpack our relationship with sweetness in the context of modern nutrition and health.
Understanding Sugar Cravings and Their Impact
Sugar cravings are a common phenomenon experienced by many individuals, often linked to the consumption of ultra-processed foods. These foods not only contain high levels of added sugars but also unhealthy fats and sodium, which enhance their palatability. As a result, people find themselves reaching for sugary snacks and drinks more frequently. The human brain has evolved to seek out sweet flavors as a survival mechanism, which can explain why sugar can feel irresistible at times. Understanding the biology behind sugar cravings is essential for developing healthier eating habits.
In addition to biological factors, environmental influences play a significant role in triggering sugar cravings. The omnipresence of sugary treats in our diet, especially in processed foods, can lead to habitual consumption patterns that are hard to break. When individuals try to reduce their sugar intake, they may face withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches, anxiety, and mood swings. This discomfort can deter many from successfully reducing their sugar consumption. Moreover, the psychological aspect of cravings must not be overlooked; emotional eating can compound the struggle, making it essential for people to adopt strategies that tackle both the physical and mental components of sugar cravings.
Is Sugar Addictive? The Debate Continues
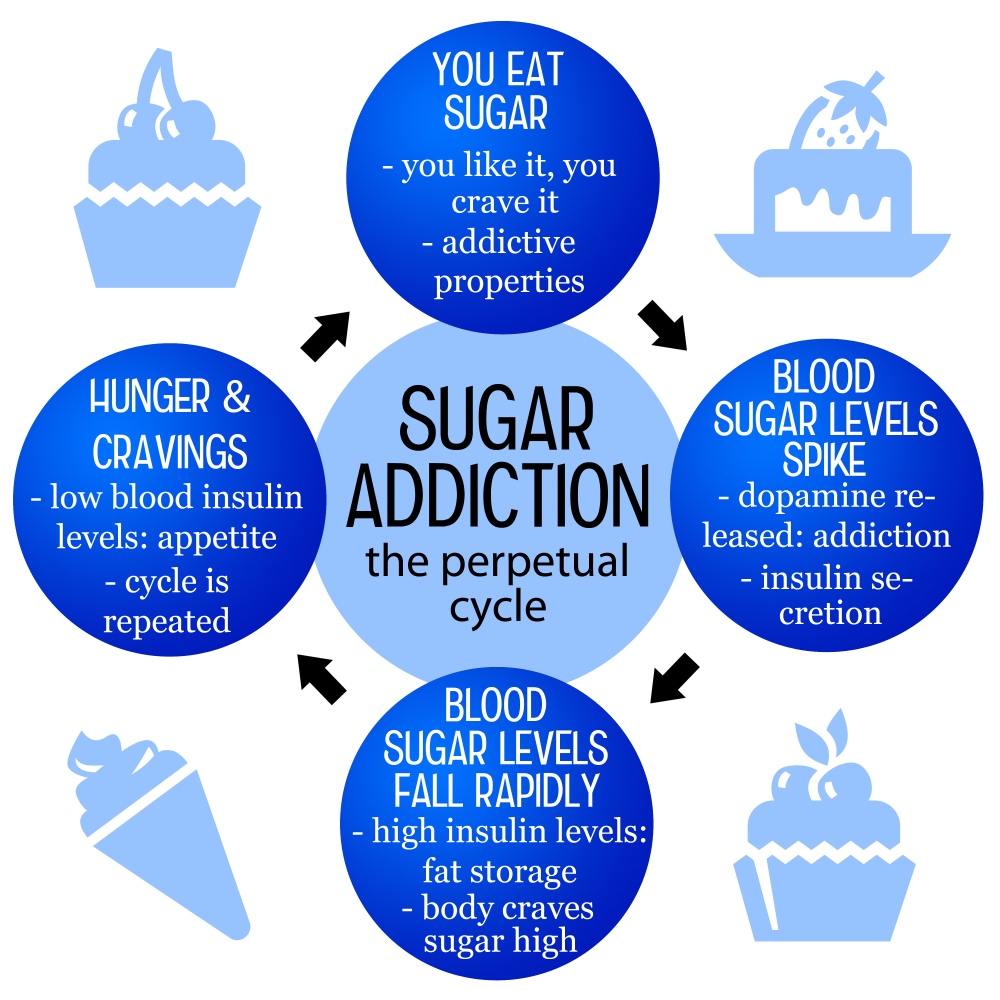
The question of whether sugar is truly addictive remains a provocative topic among nutrition experts. While substances like alcohol and nicotine are classified as addictive based on strict clinical criteria, sugar does not meet these same standards. However, research indicates that sugar can lead to increased cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, similar to those seen with addictive substances. This has led some to argue for a reclassification of sugar in discussions about addiction. Those who argue for the addictive nature of sugar often point to the way it can create a cycle of bingeing and withdrawal that is evocative of classic addiction experiences.
While sugar may not be classified as an addictive substance, the health effects of sugar cannot be overlooked. High sugar consumption is associated with various negative health outcomes, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. As the average American consumes almost 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, it’s crucial to recognize the potential harm of such consumption levels. The addictive-like qualities of sugar highlight the importance of moderation and awareness regarding sugar intake. Making educated choices about diet and reducing added sugars gradually, rather than going cold turkey, can help manage cravings without severe withdrawal symptoms.
Health Effects of Sugar on the Body
The health effects of sugar are multifaceted and often concerning. A diet high in added sugars has been linked to obesity, metabolic syndrome, and even cardiovascular diseases. Consuming excessive amounts of sugar can lead to insulin resistance, which paves the way for type 2 diabetes. Moreover, sugary foods and drinks can promote inflammation and contribute to liver damage over time. This makes it essential for individuals to monitor their sugar intake to avoid these serious health consequences.
In addition to physical health issues, high sugar consumption can lead to negative psychological effects. Some studies have indicated that diets high in sugar may be associated with an increased risk of depression and anxiety. This is partly due to the way sugar affects brain chemistry and its role in inflammatory processes. Therefore, addressing sugar consumption not only has implications for physical health but also for mental well-being. Education on reading food labels and being conscious of hidden sugars in processed foods can significantly impact overall health.
Processed Foods and Sugar Intake
Processed foods are a significant source of hidden sugars in our diets. These foods often contain added sugars in large quantities, which can contribute to a host of health issues. Food manufacturers use sugars not just for sweetness but also to enhance flavor and improve texture, making these products more appealing. This reliance on sugar in processed foods can lead to overeating and a lack of nutrient diversity in our diets, as whole foods rich in essential nutrients are often replaced with sugar-laden options.
Moreover, the prevalence of processed foods contributes to the normalization of high sugar consumption in daily life. It’s not unusual for snacks, desserts, and even savory items to contain hidden sugars, further complicating efforts to manage sugar intake. A conscious effort to choose whole, unprocessed foods can help individuals reduce their consumption of added sugars. Focusing on whole fruits, vegetables, and grains provides essential nutrients without the excessive sugars found in many processed foods.
Managing Sugar Withdrawal Symptoms
When individuals decide to cut back on sugar, they may experience withdrawal symptoms that can mimic those associated with more traditional addictive substances. Symptoms like headaches, fatigue, and irritability can arise as the body adjusts to a lower sugar intake. Understanding that these symptoms are temporary and part of the body’s adjustment process can help individuals stay committed to their goals. Gradual reduction of sugar, rather than an abrupt elimination, tends to mitigate the intensity of these withdrawal symptoms.
Employing strategies such as incorporating alternative sweeteners or increasing protein and fiber intake can also help in managing these symptoms. Additionally, staying hydrated and maintaining balanced meals can support overall wellness during this transition. Being aware of the potential for sugar withdrawal symptoms helps prepare individuals mentally and physically as they strive for a healthier diet, making the journey toward reducing sugar intake less daunting.
The Importance of Moderation in Sugar Consumption
Moderation is crucial when it comes to sugar consumption. While sugar can enhance flavor and provide a quick source of energy, overindulgence can lead to serious health consequences. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar intake to no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 for women. This recommendation highlights the importance of being mindful of sugar consumption in daily diets. Recognizing that sugar is present in many foods, including those that may not seem sugary, is vital in maintaining a balanced diet.
Furthermore, adopting a mindset focused on moderation rather than restriction can foster a healthier relationship with food. Instead of labeling sugar as completely off-limits, individuals can learn to enjoy it in moderation, allowing them to satiate cravings without overconsumption. This balanced approach not only helps in avoiding sugar-related health issues but also promotes long-term adherence to a healthy lifestyle.
Identifying Hidden Sugars in Everyday Foods
Identifying hidden sugars in everyday foods is a key component of maintaining healthy sugar levels. Many processed foods contain added sugars that are not immediately obvious from their packaging. Ingredients such as high fructose corn syrup, cane sugar, and even natural sweeteners like agave syrup can contribute significantly to overall sugar intake. By becoming adept at reading nutrition labels, consumers can make informed choices that align with their health goals.
Incorporating a variety of whole foods into the diet, such as fruits and vegetables, is an excellent way to avoid hidden sugars while reaping nutritional benefits. Whole foods contain natural sugars that are accompanied by fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them a healthier choice compared to processed options. By prioritizing these nutrient-dense foods, individuals can satisfy their sweet tooth in a healthier way, reducing their dependency on added sugars found in many processed foods.
The Role of Sugar in a Healthy Diet
Sugar, while often vilified, plays a role in a balanced diet when consumed in moderation. Natural sugars found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products provide essential energy and nutrients beneficial for health. These foods, which naturally contain sugars, are integral to a balanced diet and support overall well-being. Hence, the emphasis should be on distinguishing between naturally occurring sugars and added sugars found in many processed foods.
Moreover, sugar can enhance the sensory qualities of foods, making them more enjoyable to eat. This enjoyment can contribute to emotional satisfaction and a positive relationship with food. Allowing for moderate amounts of sugar in a healthy, varied diet can enhance flavor and improve meal pleasure without detrimental health effects. This balanced approach supports the notion that food should be enjoyable and nutritious.
The Ongoing Research on Sugar Addiction
Research on sugar addiction continues to evolve as scientists delve into its effects on the brain and body. Emerging studies suggest that sugar may activate the brain’s reward center, similar to other addictive substances, leading to cravings and repetitive behaviors. Understanding the biochemical pathways associated with sugar consumption can further help in addressing public health concerns related to obesity and metabolic diseases. This ongoing research underscores the complexity of sugar’s relationship with human health.
As scientists continue to explore the implications of sugar on addiction, nutrition education becomes paramount. Increasing awareness about the potential impacts of sugar on cravings can help individuals make more informed dietary choices. Furthermore, dispelling myths surrounding sugar addiction can assist in developing effective strategies for reducing sugar intake. Ultimately, the goal is to foster a healthier understanding of sugar in our diets, focusing on moderation and informed consumption.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive in the same way as alcohol or nicotine?
Sugar is often debated regarding its addictiveness. While it may increase cravings and lead to compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. The cravings caused by sugar can be attributed to the consumption of ultra-processed foods high in added sugar, which can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms when consumed less frequently.
What are the health effects of sugar and its addictive qualities?
The health effects of sugar largely depend on the amount consumed. Although sugar can enhance flavor and pleasure in food, excessive intake—averaging nearly 20 teaspoons daily in the U.S.—can lead to negative health outcomes. It exhibits some addictive qualities, which may lead to cravings, but it is not classified as an addictive substance. Moderation is key to preventing health issues associated with high sugar intake.
How do sugar cravings relate to processed foods?
Sugar cravings are often intensified by the consumption of processed foods that are engineered to be highly palatable. These foods not only contain added sugars but also unhealthy fats and sodium, which can lead to habitual consumption. When individuals attempt to reduce their intake of these foods, they may experience cravings and withdrawal-like symptoms due to the sudden drop in pleasurable foods.
What are common sugar withdrawal symptoms?
Common sugar withdrawal symptoms may include headaches, dizziness, and anxiety. These symptoms arise when reducing or eliminating sugar intake, particularly from ultra-processed foods. While these symptoms can be uncomfortable, they are typically less severe compared to those experienced with the withdrawal from substances like alcohol or nicotine.
Can reducing sugar intake improve health?
Yes, reducing sugar intake can significantly improve health. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 teaspoons for women. Lowering sugar intake can help mitigate cravings, decrease calorie consumption, and promote overall well-being by reducing the risk of diseases linked to high sugar levels.
Is it possible to eliminate sugar completely from your diet?
While you can eliminate added sugars from processed foods, completely removing all sugar from your diet is impractical and unnecessary since sugar is naturally present in many healthy foods like fruits, vegetables, and dairy. It’s crucial to strike a balance by moderating added sugar while still enjoying foods that contain natural sugars.
What role does awareness of sugar consumption play in health?
Awareness of sugar consumption is critical for maintaining health. By reading food labels and understanding the sugar content in snacks and drinks, individuals can make healthier choices. Being informed about the amount of sugar consumed daily helps in managing cravings and reducing the risk of health complications associated with excessive sugar intake.
How can one manage sugar cravings healthily?
To manage sugar cravings healthily, it’s advisable to gradually reduce the intake of added sugars rather than going cold turkey. Incorporating more whole foods, drinking water, and consuming balanced meals can help curb cravings. Mindful eating practices, where attention is given to hunger cues and food choices, also aid in overcoming sugar cravings and maintaining healthy eating habits.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Is Sugar Addictive? | Cravings exist for sugar, but it’s not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. |
| Nutrition Research Insights | Frank Hu, a nutrition expert, emphasizes the complex nature of sugar’s effects on the body and mind. |
| Comparison to Other Substances | Sugar can cause cravings and withdrawal-like symptoms but to a lesser extent than addictive drugs. |
| Ultra-Processed Foods | Many processed foods contain added sugars which heighten cravings and lead to habitual consumption. |
| Sugar’s Role in Diet | Sugar is essential in moderation, found in many nutrient-rich foods; however, high added sugar intake is concerning. |
| Recommendations | The American Heart Association suggests limiting added sugar to 9 teaspoons for men, 6 for women, and less for children. |
| Awareness & Reduction | Consumers should read labels and reduce sugar gradually to avoid withdrawal symptoms. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? The debate continues among researchers and health experts. While sugar can provoke cravings and compulsive eating behavior similar to addictive substances, it is not classified as addictive under clinical guidelines. It significantly impacts our health, especially when consumed in high amounts through ultra-processed foods, but it also plays a necessary role in our diet when consumed in moderation. Awareness of sugar intake, along with an understanding of its effects, can help manage cravings without labeling sugar as strictly addictive.